Have you ever attended a concert right when it opened for ticket sales? Or possibly waited with bated breath for the launch of the latest mobile phone? Supply and demand here in action.
It’s all about supply and demand-they matter greatly, and importantly, they’re really true that they affect businesses and consumers even lawmakers. So how? As they say, supply and demand graphs give a perfect visual to these forces. It shows the prices up to quantities. It’s quite a big deal.
Understanding the Basics of Supply
Supply is it-alpha-and-omega of economics. Let’s just dive in.
What is Supply in Economics?
Supply is the amount of want from the companies to sell things at a certain price. Just think of that supply as what’s available to them. Many things change it: production costs, continuity of new technology, and the number of sellers.
The Law of Supply: Price and Quantity Relationship
That is the law of supply: as price increases, a seller increases his desire to sell more. It’s a direct relationship. For instance, the more expensive wheat is, the more farmers will grow and sell it.
Understanding the Basics of Demand
Let us now talk about demand, the other equally crucial economic concept.
Demand in Economics
In economics, demand refers to different quantities of workout that people demand to buy at various prices. Demand is influenced by the income of consumers. The tastes of people matter a lot. They also matter expectations and prices of the same goods consumed.
The Law of Demand: Price and Quantity Relationship
Here’s a law: as prices get up, they want much less of something, usually; this is an inverse relation. A great example of this is gas; when gas prices go up, people may decide to drive less.
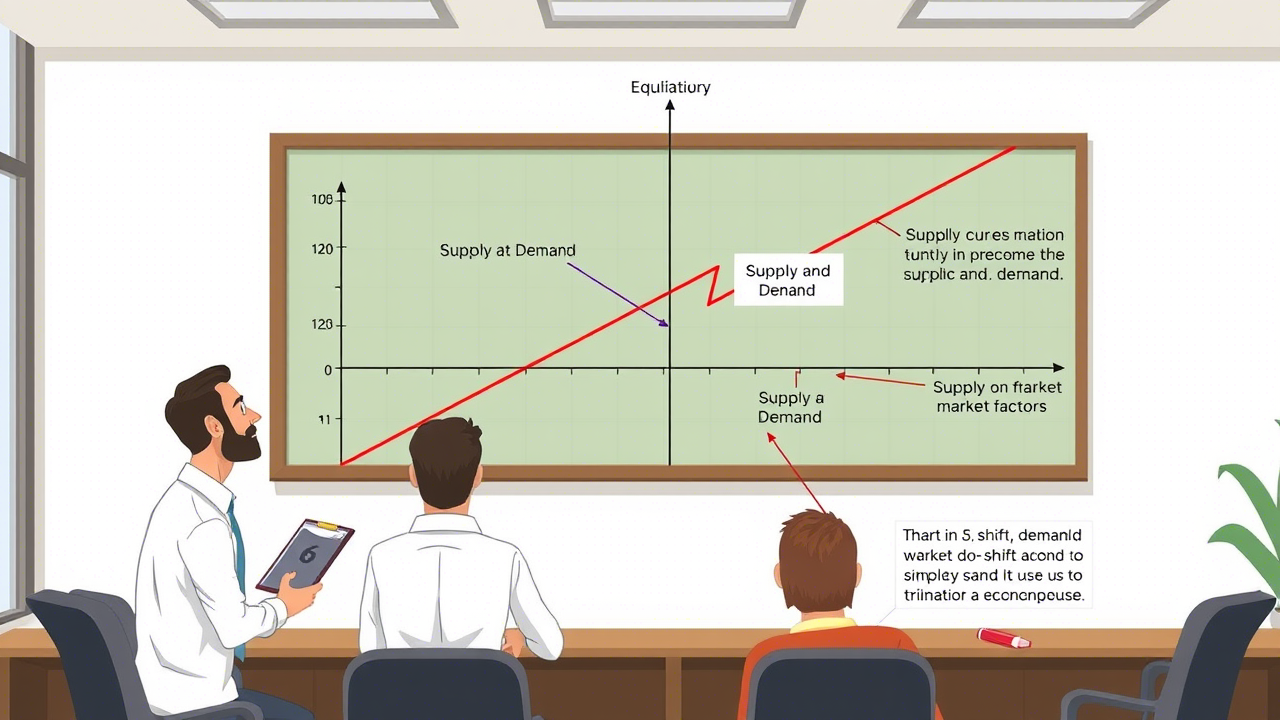
Constructing the Supply and Demand Graph
Ready for graph-making? It has proved more straightforward than you think.
Plotting the Supply Curve
So put price on the Y-axis (up and down): down along quantity on the X-axis (side to side). The supply curve slopes upward. It shows how quantity goes up as the price increases.
Plotting the Demand Curve
Again, price on Y-axes and quantity on X-axis. Again, that demand curve slopes downward. It shows that as price goes up, demand goes down.
Equilibrium: Where Supply Meets Demand
So, what happens when the two lines cross? That’s where the magic happens.
Defining Market Equilibrium
The point of crossing of the two lines is called market equilibrium. Call it equilibrium price at that point? Call it equilibrium quantity.
How Did Equilibrium Happen?
Markets always try to equalize prices. There is too much stuff with price drops and not enough price climbs. These factors would push the market toward balance.
Shifts in Supply and Demand Curves
Sometimes, everything happens, and the whole curve moves.
Why Supply Curve Shifts
New tech can boost supply. Input costs affect it. Taxes or subsidies can impact it on supply also. A shift will change equilibrium price and quantity.
Shifts in Demand Curve due to Why
So the demand may increase if people suddenly have more money with them. Changes in taste do matter. Future expectations play a part. Related goods’ prices too change demand. These also change price and quantity.
Examples and Applications in the Real World
Let’s see how supply and demand actually works.
Effects of Government Policies: Price Floors and Ceilings
Governments sometimes set price floors, like minimum wage. Or price ceilings, like rent control. These can mess with the market and cause unexpected issues.
Analyzing Market Trends with Supply and Demand
What about change in housing market? Or possibly jumps in oil price. Supply and demand analysis could tell so much more about the market movement. It’s exerting its force all the time.
Conclusion
Key concepts are supply, demand, and equilibrium. Then they would show you how the market works. By knowing all of these, good decisions on spending would be made. Remember: supply and demand change every time, every hour.